ALTAX® Neo
Utilizes the Cyclo Reducer mechanism Compact gearmotor with high shock resistance
- Utilizes our unique Cyclo Reducer mechanism for durability and long product life.
- Allows for smooth, rolling contact with no teeth breakage, resulting in high-shock resistance.
- Unlike general gearmotors, the concentric shaft direction of both the motor and output shafts result in a compact flange.
| Output Shaft | Solid Shaft |
| Output Shaft Direction | Universal |
| Mounting Method | Flange Mount, Foot Mount |
| Number of Sizes | 12 sizes (output stage) |
| Reduction Ratio | 3 - 1003 |
| Motor Capacity | 40 W - 3.7 kW |
| Motor Types | Three Phase, Premium Efficiency, High Efficiency,For Inverter, Single Phase, Outdoor, Waterproof, Increased Safety Explosion Proof, Overseas Standards |
Key Product Facts
Long
life
Unique gear mechanism ensures long life
Low
noise
Unique structure enables quiet operation
Smallest
Flange dimensions (Flange type)
High-shock resistance
Utilizes the Cyclo Reducer mechanism. Combined with the unique circular-tooth profile for the internal gear, a smooth rolling contact is established without breakage, resulting in high shock resistance.
Low noise
With the reduction mechanism firmly supported from both sides, along with its unique gear tooth count and gear mesh, low operational noise is achieved.
Smallest flange size in the industry (Flange type)
Unlike general gearmotors, the concentric shaft direction of both the motor and output shafts result in a compact flange.
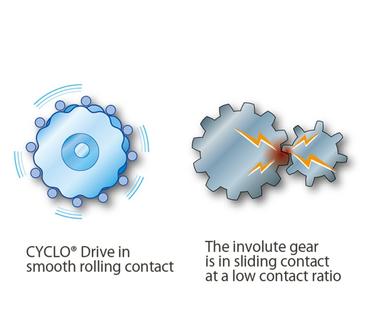
High-shock resistance
Altax Neo is a small-sized gearmotor that utilizes the Cyclo Reducer mechanism.
The Cyclo Speed Reducer features an ingenious mechanism that uses a cycloid disc with a unique smooth curve (epitrochoidal parallel curve), different from involute-tooth gear. This, combined with its unique circular tooth profile for the internal gear, allows for smooth rotating contact without tooth breakage, resulting in high shock resistance.
It also achieves a high reduction ratio with fewer reduction stages, resulting in high efficiency while simultaneously achieving a high reduction ratio.




